Table of Contents
Is your game stuttering even with good temps? CPU power limit throttling might be the hidden enemy destroying your frame times.
Don’t let locked wattage caps ruin your plays. Unlock your hardware’s full potential and get the smooth performance you need to win.
Key Takeaways
- Identify if CPU power limit throttling is causing stuttering using HWiNFO64 sensors.
- Eliminate lag by raising PL1 and PL2 power limits in your BIOS or using Intel XTU.
- Optimize unlocked CPUs with Throttlestop and disable C-States for consistent FPS.
- Unlock 12th-14th Gen Intel CPUs to sustain max boost clocks during intense gaming.
- Validate your smoother gameplay and reaction times on Joltfly’s Aim Trainer.
Diagnosing the Stutter: Distinguishing Power Throttling from Thermals
Stuttering in your favorite competitive games can be a frustrating roadblock to victory. You might instantly blame high temperatures, but your CPU’s power limits could be the real culprit. It’s crucial to distinguish between these two forms of throttling to pinpoint and fix the issue.
Thermal throttling is well-known. Your CPU intentionally slows down when it gets too hot, protecting itself from damage. This often manifests as a gradual performance drop as temperatures climb.
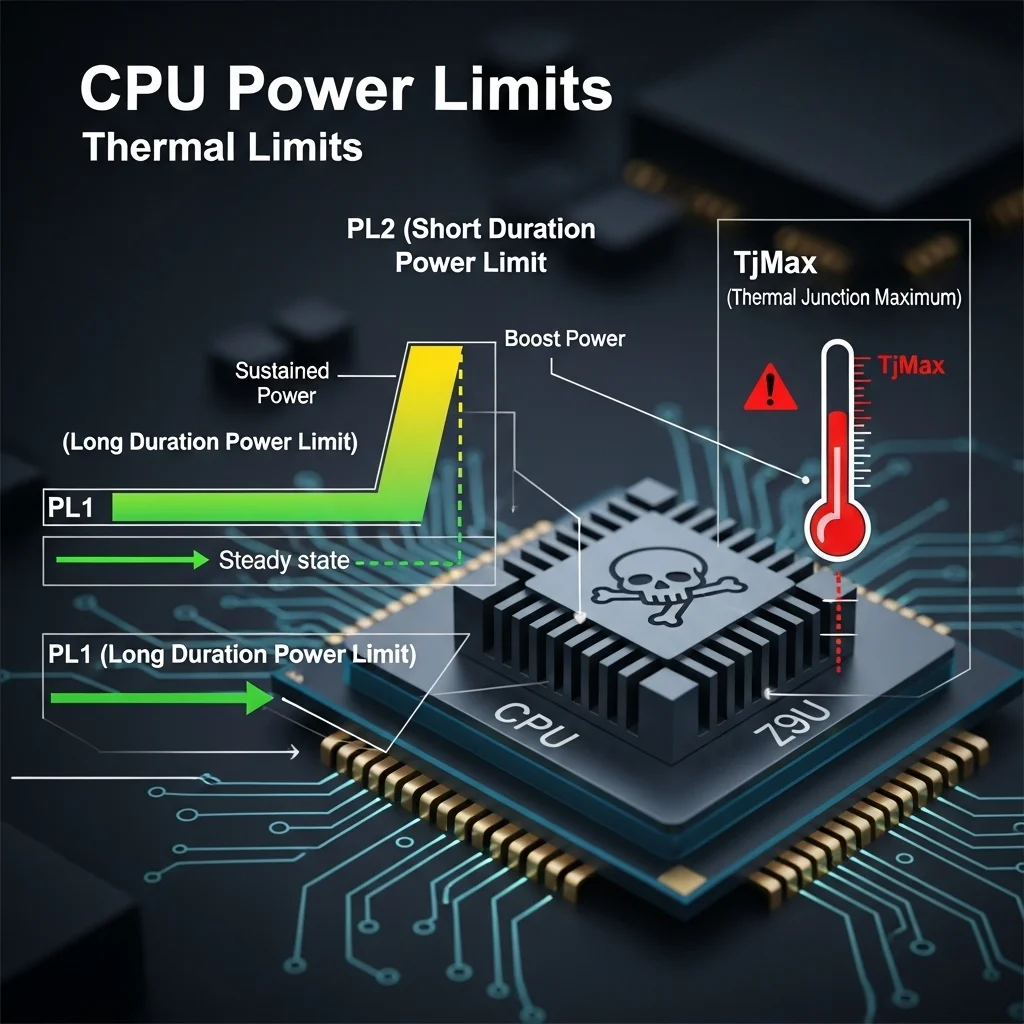
Power limit throttling is a bit more subtle, but just as disruptive. Your CPU is designed to operate within specific power envelopes, defined by limits like PL1 (long-term) and PL2 (short-term).
When your CPU tries to pull more power than these limits allow, it gets reined in. This can happen even if your temperatures are perfectly acceptable. The result? Sudden, jarring stutters that feel like mini-freezes.
The Key Differences in Your PC’s Behavior
Identifying the exact cause requires careful monitoring. Think of yourself as a detective, gathering evidence from your system’s performance metrics. The signs are there if you know what to look for.
Thermal throttling directly correlates with rising temperatures. As your CPU hits its maximum thermal junction (TjMax), performance drops. You’ll see CPU core temperatures nearing 90-100°C.
Power limit throttling, however, will show your CPU package power hitting its defined limits, like 125W or 253W for Intel CPUs, regardless of whether temperatures are dangerously high.
The performance drop can be instantaneous as the CPU adheres to these power caps. This distinction is vital for effective troubleshooting and optimizing your gaming rig.
Monitoring Tools for Precise Diagnosis
To diagnose, you need the right tools. Software like HWiNFO64 or HWMonitor is your best friend here. These programs provide real-time data on your CPU’s vitals.
- CPU Package Power: This metric shows how much power your CPU is currently drawing. Watch for it hitting its PL1 or PL2 limits.
- Core Clocks: Observe if clock speeds suddenly drop when power limits are hit, even with moderate temperatures.
- Core Temperatures: While important, remember they might not be the primary trigger if power throttling is active.
- “Limit Reasons” Sensor: HWiNFO64 often displays specific “Limit Reasons” that clearly indicate if your CPU is throttling due to PL1, PL2, or thermal reasons.
By tracking these metrics during an intense gaming session or a CPU stress test, you can identify the exact bottleneck. This data empowers you to take targeted action.
A study by TechSpot in October 2023 emphasizes that understanding these power limits, such as PL1 and PL2, is critical for getting consistent performance from modern CPUs.
A bar chart showing common CPU limiting factors under load: Power Limit (PL1/PL2) at 60%, Thermal Limit (TjMax) at 30%, Voltage Limit at 5%, and Other (e.g., VRM) at 5%.
Actionable Steps to Conquer Stuttering
Once you’ve diagnosed the culprit, it’s time to act. If thermal throttling is the issue, improve your cooling. Clean your CPU cooler, apply fresh thermal paste, or consider upgrading your heatsink or case fans.
For power limit throttling, things get a bit more technical. You might need to adjust your motherboard’s BIOS settings to raise PL1 and PL2 limits. Be cautious, as this requires adequate cooling and a robust power delivery system (VRM).
Overclocking your system without proper consideration of these limits can often exacerbate stuttering. Learn how to optimize your system without introducing new forms of lag with our guide on reducing controller input lag with PC overclocking.
Remember, a stable system is a winning system. Don’t let confusing metrics hold back your climb to the top of the leaderboards.
Ready to test the impact of your optimizations? Head over to Joltfly and challenge your skills. Try our Aim Trainer & Mouse Accuracy Test to see how a stutter-free system enhances your precision and reaction time.
Understanding PL1, PL2, and EDP Limits in Modern Games
To dominate in competitive gaming, every millisecond and frame counts. CPU power limit throttling is a silent killer of performance, often causing frustrating stuttering.
Understanding Power Limit 1 (PL1), Power Limit 2 (PL2), and Electrical Design Point (EDP) limits is crucial. These are the rules your CPU follows to manage its power draw and heat output.
PL1: Your CPU’s Sustained Power Target
PL1, or Power Limit 1, defines the maximum power your CPU can draw continuously for an extended period. Think of it as your CPU’s long-term endurance target.
This limit directly influences your CPU’s base clock speed and sustained performance in demanding games or during intense tasks.
When your CPU hits its PL1 limit, it downclocks to stay within that thermal and power envelope. This can lead to noticeable frame drops and stuttering in your favorite titles.
PL2: The Short-Burst Power Boost
PL2, or Power Limit 2, is your CPU’s temporary burst power limit. It allows your CPU to draw significantly more power for a short duration, usually seconds to tens of seconds.
This temporary boost is vital for handling sudden, intense workloads, like loading a new game area or a quick, demanding combat sequence.
Once the PL2 duration expires, your CPU will drop back down to its PL1 limit. If this happens frequently during gaming, you’ll experience intermittent stuttering as your performance fluctuates.
EDP Limits: Current and Voltage Constraints
EDP limits refer to electrical design points, which include limits on current (Amperes) and voltage delivery to your CPU. These are secondary safety nets, often tied closely to PL1 and PL2.
Even if your CPU hasn’t hit its PL1 or PL2 wattage limit, it can still throttle if it exceeds its maximum current or voltage ratings. This ensures component longevity.
Hitting an EDP limit can also cause immediate performance drops, leading to the same frustrating stuttering issues that power throttling creates.
The Gaming Impact: Stuttering and FPS Drops
When your CPU repeatedly hits these power or EDP limits, it struggles to maintain consistent clock speeds. This inconsistency directly translates into unpredictable frame times.
In competitive games, unstable frame times manifest as stuttering. This can make aiming difficult, reactions sluggish, and ultimately cost you crucial plays.
For gamers seeking peak performance, ensuring your CPU has adequate headroom and proper cooling is non-negotiable. Don’t let power limits hold you back.
A bar chart showing the impact of CPU power limits on average gaming FPS. Unlimited power yields 100 FPS, default PL1/PL2 results in 90 FPS, and strict PL1 only results in 75 FPS.
Optimizing Your CPU for Consistent Performance
You can often adjust PL1, PL2, and their duration in your motherboard’s BIOS/UEFI settings. Higher limits allow for more sustained boost performance.
Always exercise caution when modifying these settings. Ensure your CPU cooler can handle the increased heat generated by higher power draws.
Monitoring your CPU’s temperature and power draw with tools like HWMonitor or Intel XTU is crucial after making adjustments. You want to avoid thermal throttling.
Consider these steps to optimize your system:
- Update BIOS: Newer BIOS versions can sometimes offer improved power management profiles.
- Enhance Cooling: A high-performance CPU cooler is paramount for maintaining boosted clock speeds.
- Adjust Limits: Increase PL1 and PL2 targets within safe thermal limits in your BIOS.
- Monitor Temps: Use software to watch CPU temperatures and clock speeds during demanding gameplay.
- Power Plan: Set your Windows Power Plan to ‘High Performance’ or ‘Ultimate Performance’.
For other performance optimizations, explore guides on topics like optimizing RAM timings and frequency to squeeze every drop of power from your rig.
Don’t let hidden power limits throttle your potential. Take control of your CPU’s performance. Head over to Joltfly’s Device Tests to check your system’s stability and push your hardware to its limits. Challenge your gaming circle to see who can maintain the most consistent framerates!
In Short
- CPU stuttering in games can be caused by either thermal throttling due to high temperatures or power limit throttling from exceeding defined power caps like PL1/PL2.
- Distinguishing the two requires monitoring CPU package power, core temperatures, and “Limit Reasons” using tools like HWiNFO64.
- Thermal throttling is addressed by improving cooling, while power limit throttling may require adjusting PL1/PL2 limits in the BIOS with caution.
Optimizing Unlocked Systems: Throttlestop and BIOS C-States
Your gaming rig can hit a wall.
CPU power limit throttling causes frustrating stuttering. Your processor cuts speed to stay within thermal or electrical limits.
This kills your competitive edge with inconsistent frame rates.
It’s common, especially with powerful CPUs in compact systems. But for unlocked systems, you have potent tools.
You can fight back and reclaim lost performance. Dominate throttling, not be dominated by it.
This section shows you how. We’ll dive into Throttlestop and BIOS C-States.
These are your weapons to stabilize frame rates. Push your CPU to its maximum potential. Get ready to enhance your skills.
Unleashing Your CPU with Throttlestop
Throttlestop is a powerful, free utility for Windows. It lets you monitor and tweak your CPU’s behavior.
This tool is a game-changer. It prevents power limit throttling and maximizes performance.
It gives you granular control over various CPU parameters. You can effectively bypass artificial limits.
This ensures consistent, peak performance during intense gaming sessions.
Key features include undervolting and adjusting Turbo Power Limits. You can also disable CPU power saving features.
These efforts reduce heat and improve stability, giving you the edge.
Core Throttlestop Optimizations
- Disable BD PROCHOT: This setting prevents your CPU from throttling based on other system component temperatures. It’s a common fix for unnecessary throttling.
- Adjust Turbo Power Limits: Increase these limits. Your CPU can then sustain higher clock speeds for longer. This directly tackles power limit throttling.
- Undervolting (FIVR): Reduce the voltage supplied to your CPU while maintaining stability. Lower voltage means less heat. This reduces the likelihood of thermal throttling.
- Disable C1E and SpeedStep: These power-saving features can cause momentary dips in CPU performance. Disabling them ensures your CPU stays at high clock speeds.
Monitoring your CPU’s temperature and performance metrics is crucial.
Tools within Throttlestop help you track core temps and clock speeds. This ensures stability and optimal tuning.
Mastering BIOS C-States for Peak Performance
Beyond software, your BIOS holds critical settings. These impact CPU power directly.
C-States are CPU idle power states. They’re for energy efficiency, but can cause issues.
Sometimes, they introduce latency and micro-stutter in games. That’s a performance killer.
Rapid C-State switching creates tiny delays. This causes noticeable stuttering during fast-paced gameplay.
For competitive gamers, every millisecond counts. Eliminate those delays.
Adjusting C-States in your BIOS provides a smoother experience. Keep your CPU in higher power states when gaming.
This minimizes transitions and maintains consistent performance. Gain that competitive advantage.
Configuring C-States in BIOS
Access your motherboard’s BIOS during boot-up. Look for “CPU Power Management” or similar menus.
Exact names vary by manufacturer, but the principles are consistent.
- Disable C1E Support: This is an enhanced halt state. Disabling it forces the CPU to remain in C0 (active state) more often.
- Disable Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST): This dynamically adjusts CPU clock frequency and voltage. For maximum gaming performance, keep it off.
- Set C-State Limit to C0: Some BIOS versions let you explicitly limit the CPU to only use the C0 state. This provides the most consistent performance.
Disabling C-States increases power consumption and heat. Be aware of this trade-off.
Ensure your cooling solution is up to the task. Test your system thoroughly after any BIOS changes.
For more advanced PC optimizations, check out our Ultimate PC Overclock Guide. It covers many ways to reduce input lag and boost your system.
Verify Your Gains with Joltfly
After fine-tuning, verify your improvements. Jump onto Joltfly’s Aim Trainer.
Feel the difference in responsiveness and consistency. Your efforts will pay off.
Notice how your gameplay is smoother. Your shots will land with more precision.
No more frustrating stutters. This is the competitive edge you’ve been chasing.
Challenge your friends to see who has the most optimized rig. Dominate your gaming circle by eliminating CPU power limit throttling for good.
In Short
- CPU power limit throttling causes frustrating stuttering and inconsistent frame rates in gaming rigs.
- Throttlestop is a powerful utility for Windows that optimizes CPU performance by preventing power limit throttling through undervolting and adjusting power limits.
- Mastering BIOS C-States by disabling power-saving features like C1E and SpeedStep helps eliminate micro-stutter and maintain consistent CPU performance for competitive gaming, though it increases heat and power consumption.
Bypassing Restrictions on Locked CPUs (12th-14th Gen Intel)
Your high-performance Intel CPU is a beast. But sometimes, even your 12th, 13th, or 14th Gen processor gets held back. Power limit throttling can turn your smooth gameplay into a stuttering mess, costing you critical frames.
You need every advantage to dominate. Understanding and bypassing these factory restrictions can unlock your CPU’s true potential. Get ready to boost your competitive edge.
Unlocking Your CPU’s Full Power
Intel’s “locked” CPUs, especially non-K SKUs, are often limited by strict power policies. Even K-series processors can face limitations depending on your motherboard’s default settings.
These limits, known as Power Limit 1 (PL1) and Power Limit 2 (PL2), dictate how much power your CPU can draw over specific durations. When exceeded, your CPU throttles, leading to performance drops and frustrating stuttering.
Bypassing these restrictions allows your CPU to maintain higher clock speeds for longer. This translates directly to more consistent FPS and a smoother, more responsive gaming experience.

The Power Limit Game: PL1, PL2, and Tau
Think of PL1 as the long-term power budget. PL2 is a higher, short-term burst limit. Tau is the duration for which PL2 can be sustained.
When your CPU hits PL1 or PL2, it scales back its performance to stay within those wattage boundaries. This keeps temperatures in check but bottlenecks your system.
For competitive gaming, consistent peak performance is non-negotiable. You want your CPU to always deliver its best, without artificial shackles.
A bar chart showing typical CPU power draw for an Intel i9-13900K: Intel Max Turbo Power (Default) is 253W, while Unlocked (Typical Gaming Load) can reach 290W.
As seen in independent testing, removing these limits can significantly increase the power draw. For example, an Intel i9-13900K typically peaks at 253W under Intel’s Max Turbo Power specification. However, with power limits removed, it can average around 290W under typical heavy gaming loads, according to reviews like those on Tom’s Hardware.
This extra wattage directly fuels higher, sustained clock speeds.
How to Bypass Power Limits for Peak Performance
There are a few key ways to unleash your CPU. These methods primarily involve adjusting settings in your motherboard’s BIOS/UEFI or using Intel’s XTU software.
1. BIOS/UEFI Settings (Recommended)
This is the most effective way to gain control. Restart your PC and press the DEL or F2 key to enter your BIOS/UEFI.
Navigate to the ‘Overclocking’ or ‘Advanced CPU Settings’ section. Look for options related to ‘Long Duration Power Limit (PL1)’, ‘Short Duration Power Limit (PL2)’, and ‘Tau’.
Set PL1 and PL2 to their maximum possible values, often up to 4096W or “Unlimited”. Also, set Tau to its maximum, or disable it if the option exists. Some motherboards have a “Multi-Core Enhancement” (MCE) or “Enhanced Turbo” option that automatically removes these limits.
Enable MCE if available. This often sets the power limits to motherboard-specific, higher values, boosting performance. Save and exit your BIOS.
2. Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU)
For a software-based approach, Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) allows you to adjust power limits directly from Windows. This is a great tool for real-time monitoring and tweaking.
Download and install XTU. In the application, navigate to the “Advanced Tuning” section. You can manually increase the ‘Processor Core IccMax’, ‘Turbo Boost Power Max’ (PL2), and ‘Turbo Boost Short Power Max’ (PL1).
Remember that BIOS settings usually override XTU, so it’s best to configure in the BIOS first for a persistent solution.
Critical Considerations Before You Dive In
Unlocking power limits boosts performance, but it generates more heat. Ensure your cooling solution, whether air or AIO, is up to the task.
Monitor your CPU temperatures with tools like HWMonitor or Core Temp. Keep temperatures below 90-95°C during heavy load to maintain stability and CPU longevity.
This process can also impact system stability. If you experience crashes, revert your settings incrementally until stable. Just like optimizing your RAM timings and frequency for peak gaming, system stability is key.
- Upgrade Your Cooling: A robust cooler is paramount for higher power draw.
- Monitor Temps Constantly: Keep an eye on your CPU core temperatures.
- Test for Stability: Run stress tests and play your favorite games to confirm stable performance.
Gain the Ultimate Advantage
Bypassing CPU power limit throttling is a game-changer. It eliminates frustrating stutters and ensures your CPU delivers maximum performance when you need it most.
Unlock those hidden frames, sharpen your aim, and dominate your gaming circle. Don’t let artificial limits hold you back!
After optimizing your CPU, put your system to the test. Head over to Joltfly’s Device Tests to check your system’s response and precision.
The IMON Slope Tweak and Registry Hacks for Hard Limits
CPU power limit throttling can be a silent assassin for your in-game performance. It causes frustrating stuttering and drops your frame rates when you need them most. You’re losing out on clutch plays.
But what if you could take control? Advanced tweaks like the IMON Slope adjustment and direct registry hacks offer ways to push past these limits. Get ready to unlock your CPU’s full potential.
Unleashing Power with IMON Slope Tweak
Your CPU constantly reports its power consumption to the motherboard. This is done through a value known as IMON, or Integrated MONitor.
By default, this monitoring ensures your CPU stays within its specified power limits, like PL1 and PL2. These limits are designed for stability, but they can throttle your performance.
The IMON Slope is a configurable parameter. Tweaking it can essentially “trick” your CPU’s power controller. It makes the CPU report a lower power draw than it’s actually using.
This bypass allows your CPU to maintain higher clock speeds and boost frequencies for longer periods. The result is sustained performance, directly combating power limit throttling causing stuttering.
However, this is a powerful modification. You need to monitor your CPU temperatures closely. Overheating can damage components and lead to system instability.
Registry Hacks for Hard Limits
Beyond IMON Slope, the Windows Registry holds keys to system-level power management. These aren’t for the faint of heart, but they offer ultimate control.
Registry hacks can involve modifying entries that define hard power limits. They can force your CPU to ignore or reinterpret factory-set boundaries.
This level of direct manipulation allows you to potentially override thermal and power budgets. It ensures your CPU delivers maximum performance, even under heavy gaming loads.
For example, some gamers delve into specific power policy subkeys. They adjust values related to processor performance states and thermal management.
Before attempting any registry modification, create a system restore point. Back up your registry. One wrong move can lead to system crashes or boot failures.
While these methods are potent against CPU power limit throttling causing stuttering, they demand precision. Always research thoroughly and understand the risks.
For persistent stuttering issues, even beyond power limits, consider checking other system bottlenecks. Sometimes, the problem lies elsewhere. For example, learning how to fix shader compilation stutter on PC can save your game.
The Benefits and Risks
The primary benefit of these tweaks is eliminating performance stutter. You’ll experience smoother gameplay, higher average FPS, and better responsiveness.
This gives you a critical edge in competitive titles. You won’t be held back by artificial power ceilings.
The risks are significant, though. Incorrect IMON Slope values or registry edits can cause:
- System instability and crashes.
- Overheating, leading to CPU degradation.
- Potential hardware damage over time.
- Data corruption or loss.
Proceed with extreme caution. Your gaming rig is a finely tuned machine. Unlocking its full power requires respect for its limits.
A bar chart showing the relative gaming performance impact of CPU throttling: Without Throttling (100%), Mild Throttling (85%), and Severe Throttling (60%).
Dominate Your Gaming Circle
Mastering these advanced techniques puts you in a different league. You’re not just playing the game; you’re optimizing your entire system for victory.
After implementing these tweaks, test your system rigorously. Use benchmarking tools and play your favorite demanding titles.
Track your FPS, monitor temperatures, and check for any signs of instability. Fine-tune your settings for that perfect balance of power and reliability.
Push your skills further. Visit Joltfly to explore various trainer games and device tests. Challenge yourself to hit new highs in your Click Speed Test or Aim Trainer sessions. Show your gaming circle what true optimization can achieve!
In Short
- Intel’s 12th-14th Gen CPUs often have power limits (PL1, PL2, Tau) that restrict performance and cause throttling.
- Bypassing these power limits, primarily via BIOS/UEFI settings or Intel XTU, allows the CPU to sustain higher clock speeds for improved gaming performance.
- Unlocking power limits increases heat generation, requiring a robust cooling solution to prevent overheating.