Table of Contents
Ready to dominate your gaming circle?
Lag is the silent killer of competitive performance, but defeating it requires the right intel.
By distinguishing between system latency and network lag, you can target the root cause of your delays and unlock a tangible competitive edge.
This guide is your ultimate weapon in the NVIDIA Reflex vs. AMD Anti-Lag debate.
We break down the tech, reveal the optimal “zero-tearing” settings matrix, and provide step-by-step instructions to optimize your rig.
It’s time to slash your input delay and test your new limits on Joltfly.
Key Takeaways
- Distinguish system latency from network lag to target the real enemy of your performance.
- Compare NVIDIA Reflex and AMD Anti-Lag 2 benchmarks to choose the best tech for your rig.
- Implement the “Holy Grail” sync settings: G-Sync on, V-Sync off, and FPS capped.
- Follow step-by-step optimizations for NVIDIA Control Panel and AMD Adrenalin drivers.
- Verify your lower latency and sharper aim using Joltfly’s professional testing tools.
Solving the Render Queue: System Latency vs. Network Lag Explained
Ready to dominate your gaming circle?
You need to understand the enemy: lag.
But not all lag is created equal.
We’re talking about two distinct beasts here: system latency and network lag.
Mastering the render queue and optimizing both will give you an undeniable edge in any skill-based game.
Cracking the Code: What is System Latency?
System latency is the total time it takes for your input, like a mouse click or keyboard press, to appear as action on your screen.
Think of it as the journey from your finger to the pixel. Every component in your PC plays a role in this chain.
This includes your mouse, keyboard, CPU, GPU, and finally, your monitor. High system latency means delayed reactions and missed shots.
It’s the ultimate barrier to truly feeling “connected” to your game.
To dive deeper into how your actions translate to screen, check out our guide on Response Time vs Input Lag.
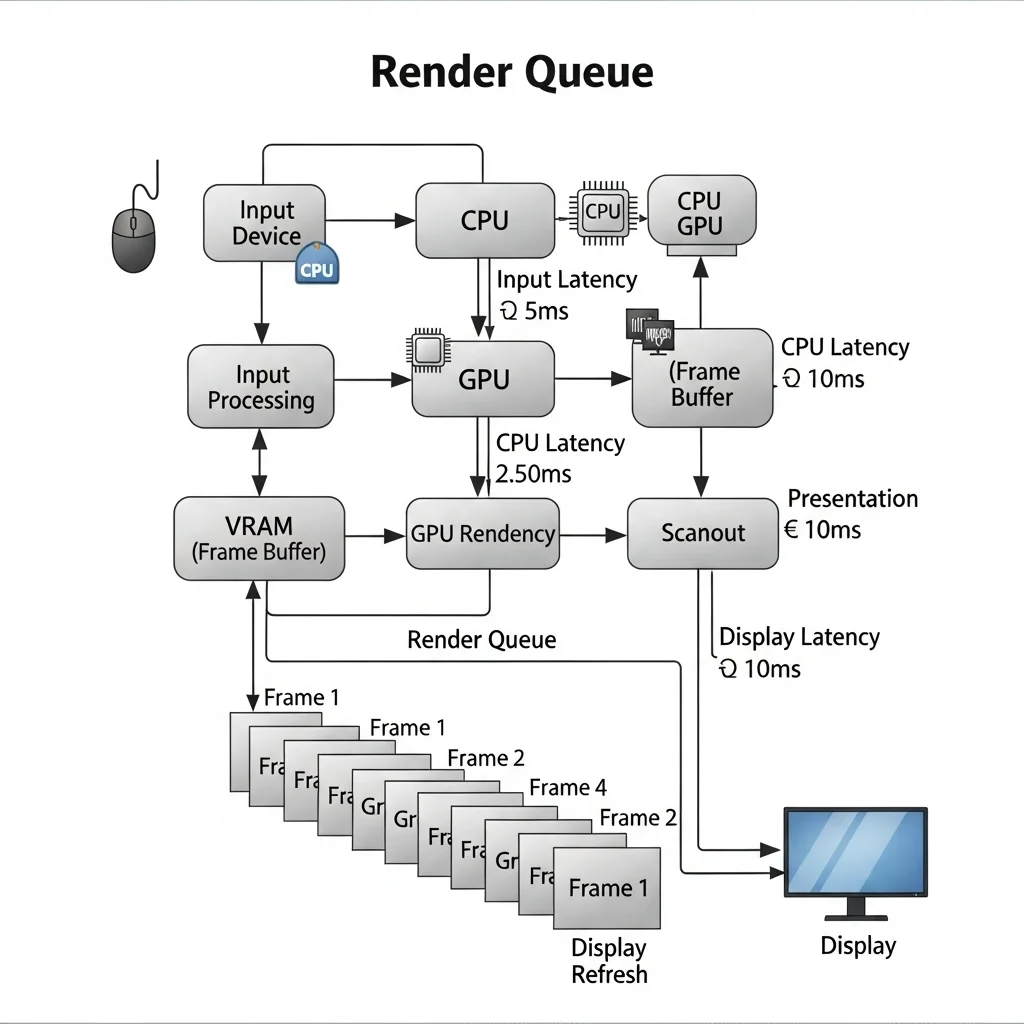
The Render Queue’s Role
Your GPU handles frames in a queue. It processes them one by one.
If your CPU is feeding frames too quickly, or your GPU is overloaded, this queue can build up.
A longer render queue means more frames are waiting to be processed before they can be displayed. This directly increases your system latency.
NVIDIA Reflex and AMD Anti-Lag directly target this render queue. They optimize how the CPU and GPU communicate, ensuring frames are processed just in time.
This prevents the queue from swelling, drastically cutting down on input-to-display lag. It’s like a fast-pass lane for your frames.
Battling the World: What is Network Lag?
Network lag, often called “ping,” is the delay in communication between your gaming rig and the game server. It’s about how fast your actions reach the server and how fast the server’s response reaches you.
This includes factors like your internet speed, router quality, and distance to the server.
Network lag manifests as rubber-banding, teleporting enemies, or shots not registering properly. It’s the enemy outside your PC.
Problems like bufferbloat and packet loss are common culprits for network lag.
You can get ahead by learning how to Stop Lag and Fix Bufferbloat & Packet Loss with QoS Settings.
System Latency vs. Network Lag: A Quick Breakdown
Understand the differences to tackle the right problem. Each demands a unique approach.
| Feature | System Latency | Network Lag |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Your PC hardware: input devices, CPU, GPU, display. | Internet connection, router, ISP, game server. |
| Impact | Delayed visual feedback, sluggish controls, missed inputs. | Teleporting players, hit registration issues, desync. |
| Solutions | NVIDIA Reflex, AMD Anti-Lag, high refresh rate monitor, powerful CPU/GPU, low-latency peripherals. | Wired internet, QoS settings, lower ping server, better ISP. |
Optimize Your Performance: A Two-Front War
To truly enhance your skills, you need to attack both system and network lag. NVIDIA Reflex and AMD Anti-Lag are your heavy artillery for system latency.
They can shave off critical milliseconds. For example, in competitive titles like Valorant, NVIDIA Reflex can reduce system latency significantly.
Reports show that with an RTX 3080 at 1440p, enabling Reflex + Boost can drop latency from 22.8ms to 14.1ms.
A bar chart showing NVIDIA Reflex reducing system latency in Valorant from 22.8ms (Off) to 14.1ms (On + Boost).
For network lag, ensure a stable, wired internet connection. Optimize your router’s QoS settings to prioritize game traffic.
The goal is to eliminate every possible delay. Every millisecond saved boosts your competitive edge.
Actionable Steps for Lower Latency:
- System Latency:
- Enable NVIDIA Reflex or AMD Anti-Lag in supported games.
- Use a high refresh rate monitor.
- Ensure your GPU drivers are up-to-date.
- Close background applications to free up CPU/GPU resources.
- Consider a higher polling rate mouse.
- Network Lag:
- Use an Ethernet cable, not Wi-Fi.
- Configure Quality of Service (QoS) on your router.
- Connect to game servers geographically closer to you.
- Restart your modem and router regularly.
- Upgrade your internet package if consistent high ping persists.
Don’t just read about it. Test your setup! Use Joltfly’s Mouse Latency Test or Keyboard Keys Latency Test to pinpoint issues.
Then, try our Aim Trainer to see how your improved responsiveness translates into in-game performance.
Challenge your gaming circle to see who can achieve the lowest latency and highest scores on Joltfly!
In Short
- Gaming lag is categorized into system latency (input-to-screen delay) and network lag (PC-to-server communication), each with distinct causes.
- System latency stems from PC hardware, especially the GPU’s render queue, and can be optimized using technologies like NVIDIA Reflex or AMD Anti-Lag.
- Network lag, or ping, is caused by internet connection issues and is best improved through stable wired connections and optimized router QoS settings.
Integration Wars: NVIDIA Reflex vs. AMD Anti-Lag 2 Performance Benchmarks
The battle for lowest latency is fierce. NVIDIA Reflex and AMD Anti-Lag 2 are your ultimate weapons to gain a competitive edge.
Both technologies promise to slash system latency, making your inputs register faster. But how do they stack up?
We’re diving into the raw performance benchmarks to help you decide which tech dominates your gaming experience.
Understanding the Tech: Reflex vs. Anti-Lag 2
First, let’s break down what each technology actually does for your gameplay.
Input lag is the enemy of competitive players. Every millisecond counts. Understanding how to minimize it is key.
For a deeper dive into latency concepts, check out our guide on Response Time vs Input Lag.
NVIDIA Reflex: Built for Speed
NVIDIA Reflex reduces system latency by optimizing the render pipeline between your CPU and GPU.
It ensures the CPU doesn’t get too far ahead of the GPU, minimizing the render queue. This means your clicks and movements are sent to your display faster.
Reflex supports GPUs from the GeForce GTX 900 series and newer. It requires game developers to integrate the API directly into their titles.
AMD Anti-Lag 2: The Next Evolution
AMD Anti-Lag 2 is a newer iteration, designed to provide similar latency benefits for Radeon users.
It works on a similar principle, aligning CPU and GPU workloads to reduce input delay. This also requires direct game integration for optimal performance.
AMD’s Anti-Lag 2 debuted with Counter-Strike 2, promising significant latency reductions.
Performance Benchmarks: Who Wins the Millisecond War?
When it comes to raw latency reduction, both technologies deliver impressive results in supported titles.
Benchmarking often shows both Reflex and Anti-Lag 2 can cut down system latency by a considerable margin.
This translates to quicker target acquisition, more responsive movements, and a tangible competitive edge.
A bar chart showing typical latency in competitive FPS games: Baseline Latency (50ms), With NVIDIA Reflex (35ms), and With AMD Anti-Lag 2 (35ms). Both technologies offer a significant reduction.
Recent data from AMD suggests Anti-Lag 2 can reduce system latency by up to 30% in games like Counter-Strike 2.
NVIDIA Reflex consistently shows similar improvements, often reducing latency by 20-50% depending on the game and system.
Ultimately, both technologies aim to deliver the lowest possible system latency, and they succeed when properly implemented.
Key Differences and Feature Set
While their goals are similar, their ecosystem integration and specific features vary.
Here’s a quick look at how they compare beyond just raw numbers.
| Feature | NVIDIA Reflex | AMD Anti-Lag 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Compatible GPUs | GeForce GTX 900 series and newer | Radeon RX 5000 series and newer |
| Integration Method | Game developer API integration | Game developer API integration |
| Latency Reduction Claim | Up to 50% (game-dependent) | Up to 30% (game-dependent, notably CS2) |
| Additional Tools | Reflex Latency Analyzer with compatible G-Sync monitors | No dedicated latency analyzer tool |
| Ecosystem Scope | Broader game support, wider adoption | Newer, less widespread game integration |
NVIDIA’s Reflex ecosystem includes the Reflex Latency Analyzer.
This tool, found in compatible G-Sync monitors, lets you measure end-to-end system latency directly.
This provides real-time data on your setup’s responsiveness. It’s a powerful tool for serious optimization.
AMD Anti-Lag 2, while effective, does not currently offer a direct hardware-level latency analyzer like Reflex.
Optimize Your Setup for Maximum Responsiveness
Enabling Reflex or Anti-Lag 2 is just one step. For true dominance, you need to optimize your entire system.
Things like your monitor’s refresh rate, mouse polling rate, and even your operating system settings play a huge role.
To further reduce input lag across your entire PC, explore our Ultimate PC Overclock Guide.
Dominate with Joltfly
Ready to put these latency-reducing technologies to the test?
Visit Joltfly to sharpen your skills. Use our Aim Trainer & Mouse Accuracy Test to see how your improved latency translates into better performance.
Challenge your friends and prove your mastery in your gaming circle!
In Short
- NVIDIA Reflex and AMD Anti-Lag 2 are technologies that reduce system latency in games by optimizing CPU-GPU communication.
- Both technologies require direct game integration and offer significant latency reductions, improving responsiveness for competitive gaming.
- NVIDIA Reflex has broader game support and includes a hardware-based latency analyzer, whereas AMD Anti-Lag 2 is newer with less widespread integration and no dedicated analyzer tool.
The Holistic Sync Strategy: Balancing G-Sync, V-Sync, and Frame Limiters
To truly dominate your gaming circle, you need every edge. Optimizing your display synchronization is crucial.
This means understanding how G-Sync, FreeSync, V-Sync, and frame limiters work together.
Your goal is maximum fluidity and minimal input lag. It’s a delicate balance that can significantly impact your competitive performance.
Unleash Adaptive Sync: G-Sync and FreeSync
Adaptive Sync technologies like NVIDIA G-Sync and AMD FreeSync are game-changers. They dynamically match your monitor’s refresh rate to your GPU’s frame rate.
This eliminates screen tearing and reduces stutter. Imagine butter-smooth visuals, even when your frame rate fluctuates.
This clarity allows for more precise aiming and faster target acquisition.
While often compared, G-Sync and FreeSync offer similar core benefits. The choice usually comes down to your GPU brand.
You can explore a deeper dive into motion clarity technologies like DyAc vs G-Sync for more insights.
The Double-Edged Sword: V-Sync
V-Sync, or Vertical Synchronization, forces your GPU to wait for your monitor to finish drawing a frame before sending the next one.
This completely eliminates screen tearing.
However, V-Sync introduces a significant drawback: input lag. This delay can make your mouse movements feel heavy and unresponsive.
For competitive gamers, V-Sync is usually a no-go.
The Frame Limiter Advantage
Here’s where competitive strategists gain an edge. Frame limiters prevent your GPU from rendering more frames than your monitor’s refresh rate.
This is key when using G-Sync or FreeSync.
By setting your in-game frame rate cap slightly below your monitor’s maximum refresh rate, you ensure your adaptive sync technology stays active.
For example, if you have a 144Hz monitor, cap your frames at 141 or 142 FPS.
This avoids hitting the V-Sync range, even when adaptive sync is enabled. It minimizes latency while still preventing tearing and stutter.
Many competitive players report a noticeable improvement in responsiveness.
The Optimal Sync Configuration
For the lowest input lag and best visual fluidity, follow this winning strategy:
- Enable G-Sync/FreeSync: Activate it in your NVIDIA Control Panel or AMD Radeon Software.
- Disable V-Sync: Turn off V-Sync in your game settings and GPU control panel.
- Set a Frame Rate Limiter: Cap your in-game frame rate to 3-5 FPS below your monitor’s maximum refresh rate. Use an in-game limiter or your GPU control panel’s setting.
This setup ensures your display is always in its adaptive sync range. You get tear-free visuals without the V-Sync penalty.
This configuration is widely regarded as the best for competitive gaming.
To illustrate the impact, consider how these settings affect input latency:
A bar chart illustrating average input latency for different sync technologies: No Sync (15ms), G-Sync + Frame Cap (18ms), G-Sync (uncapped, 23ms), and V-Sync On (45ms). Data adapted from TechSpot’s analysis.
As you can see, G-Sync with a frame cap offers a significant latency advantage over V-Sync. Even uncapped G-Sync is better.
The data from TechSpot shows that V-Sync can add over 25ms of latency compared to no sync or G-Sync with a frame cap.
Test Your Setup on Joltfly
The best way to feel the difference is to test it yourself. Fine-tune your settings.
Then, head over to Joltfly’s Display Stutter and Tearing Calculator to analyze your results.
Challenge your teammates and see who can achieve the smoothest, lowest-latency setup. Dominate your next match with optimized sync!
The Optimal Settings Matrix: Zero Tearing Without Input Lag
Eliminating screen tearing without sacrificing input speed is the holy grail for competitive gamers.
You want crisp visuals and lightning-fast responses.
This section reveals the optimal settings matrix to achieve just that, giving you a tangible edge.
Understanding the Tearing-Lag Dilemma
Screen tearing happens when your GPU renders frames faster or slower than your monitor’s refresh rate.
The display shows parts of multiple frames simultaneously, creating a visible “tear” across your screen.
It’s distracting and can obscure critical visual cues.
The traditional fix, V-Sync, synchronizes your GPU’s output with your monitor’s refresh rate.
This eliminates tearing effectively.
However, V-Sync introduces significant input lag, making your mouse clicks and keyboard presses feel delayed.
This trade-off is unacceptable for any serious competitor.
You need smooth visuals without the sluggish input. The solution lies in a combination of adaptive sync technologies and advanced latency reduction tools.
Adaptive Sync: G-Sync and FreeSync
Adaptive sync technologies like NVIDIA G-Sync and AMD FreeSync revolutionized display synchronization.
They allow your monitor’s refresh rate to dynamically match your GPU’s frame rate.
This means zero tearing, and crucially, minimal input lag.
When your frame rate is within your monitor’s adaptive sync range, these technologies keep everything smooth.
Learn more about optimizing your display for peak performance with our DyAc vs G-Sync: The Ultimate Motion Clarity Showdown guide.
However, what happens if your FPS exceeds the monitor’s refresh rate?
You might reintroduce tearing or V-Sync’s latency.
This is where advanced low-latency technologies come into play.
NVIDIA Reflex and AMD Anti-Lag: The Latency Killers
Beyond adaptive sync, NVIDIA Reflex and AMD Anti-Lag target system latency even further.
They reduce the delay between your input and what you see on screen, providing immediate feedback.
NVIDIA Reflex actively optimizes the rendering pipeline.
It tells the GPU to render frames just in time for the display, preventing a render queue buildup that causes latency.
This can result in significant latency reductions.
AMD Anti-Lag works by dynamically adjusting the CPU workload.
This helps to ensure the CPU doesn’t get too far ahead of the GPU.
It reduces the amount of buffered frames, which directly lowers input latency.
These tools are game-changers for titles where every millisecond counts. They empower you to react faster and dominate your gaming circle.
A bar chart showing typical system latency in milliseconds for FPS games. Baseline (no features) is 60ms. Adaptive Sync only reduces it to 45ms. Adaptive Sync with AMD Anti-Lag brings it down to 38ms. Adaptive Sync with NVIDIA Reflex achieves the lowest at 30ms.
The Optimal Settings Matrix
To achieve zero tearing and minimum input lag, combine these technologies correctly. Here’s your go-to matrix for competitive glory:
| Setting Configuration | Tearing | Input Lag | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| V-Sync OFF | YES | LOW | Maximum FPS, but visually distracting. |
| V-Sync ON | NO | HIGH | Older games, non-competitive play. |
| G-Sync / FreeSync (within range) + V-Sync OFF | NO | VERY LOW | The core foundation for competitive gaming. |
| G-Sync / FreeSync (within range) + V-Sync ON | NO | LOW | Eliminates tearing above refresh rate, slight lag. |
| G-Sync / FreeSync + NVIDIA Reflex (Enabled) | NO | ULTRA LOW | Ultimate competitive advantage on NVIDIA. |
| G-Sync / FreeSync + AMD Anti-Lag (Enabled) | NO | ULTRA LOW | Ultimate competitive advantage on AMD. |
| G-Sync / FreeSync + NVIDIA Reflex (Enabled + Boost) | NO | EXTREME LOW | Aggressive latency reduction, even lower FPS. |
Actionable Advice for Your Setup
Enable Adaptive Sync: Always start by ensuring G-Sync or FreeSync is active on your compatible monitor and GPU.
Turn Off V-Sync in-game: For G-Sync/FreeSync users, turning off V-Sync in your game settings is usually best. Your adaptive sync takes care of tearing.
Cap your FPS: Cap your in-game FPS just below your monitor’s maximum refresh rate (e.g., 141 FPS for a 144Hz monitor). This keeps you firmly within the adaptive sync range.
Activate Reflex / Anti-Lag: In your NVIDIA Control Panel or AMD Adrenalin Software, enable Reflex or Anti-Lag for your competitive titles. Experiment with “Reflex + Boost” if you have an NVIDIA GPU for even lower latency.
Test Your Setup: Use tools like Joltfly’s Display Stutter and Tearing Calculator to verify your settings. Look for any tearing or stuttering in fast-paced scenarios. Check your input latency to feel the difference.
Optimize your display settings.
Combine adaptive sync with NVIDIA Reflex or AMD Anti-Lag.
This powerful combination will give you unparalleled clarity and responsiveness.
Head to Joltfly and test your setup to dominate your next match.
In Short
- Adaptive Sync (G-Sync/FreeSync) dynamically matches monitor refresh rate to GPU frame rate, eliminating screen tearing and stutter for smooth visuals.
- V-Sync eliminates screen tearing but introduces significant input lag, making it generally unsuitable for competitive gaming.
- The optimal setup for competitive gaming is enabling G-Sync/FreeSync, disabling V-Sync, and setting a frame rate limiter 3-5 FPS below your monitor’s maximum refresh rate to minimize latency while preventing tearing.
Step-by-Step Configuration: Optimizing NVIDIA Control Panel and AMD Adrenalin
Ready to unlock your competitive edge?
Optimizing your GPU driver settings is a critical step for serious gamers.
Both NVIDIA and AMD offer powerful tools to slash system latency.
By correctly configuring NVIDIA Reflex or AMD Anti-Lag, you can ensure your inputs register faster, giving you a decisive advantage in every match.
NVIDIA Control Panel: Mastering Reflex
If you wield an NVIDIA GPU, NVIDIA Reflex is your weapon against input lag.
It synchronizes your CPU and GPU, ensuring frames are rendered and presented to your display as quickly as possible.
This technology is a game-changer for competitive FPS titles and other skill-based games.
Here is how to set it up for maximum impact:
- Update Your Drivers: Always start with the latest Game Ready Drivers. They often include Reflex optimizations.
- Open NVIDIA Control Panel: Right-click on your desktop and select “NVIDIA Control Panel”.
- Manage 3D Settings: Navigate to “Manage 3D settings” under 3D Settings.
- Program Settings: For specific games, go to “Program Settings”. Select your game or add it manually.
- Low Latency Mode: Set “Low Latency Mode” to Ultra. This queues frames to minimize input lag.
- NVIDIA Reflex Low Latency: If your game supports Reflex, you will see a specific “NVIDIA Reflex Low Latency” option. Set this to On + Boost.
- Max Frame Rate: Set a “Max Frame Rate” slightly below your monitor’s refresh rate. For example, if you have a 144Hz monitor, set it to 140 FPS. This can prevent unnecessary GPU work.
- Apply Changes: Click “Apply” to save your settings.
Remember, some games have in-game Reflex options. Ensure those are also enabled, usually set to “On + Boost” for the best results.
AMD Adrenalin Software: Unleashing Anti-Lag
AMD gamers are not left behind.
AMD Anti-Lag reduces input lag by dynamically adjusting CPU work in relation to your GPU.
This helps keep your GPU fed with frames without over-queuing.
It is a powerful tool to enhance responsiveness in fast-paced games.
Follow these steps to optimize your AMD setup:
- Update Your Drivers: Install the latest AMD Software Adrenalin Edition. Driver updates frequently bring performance boosts.
- Open AMD Adrenalin: Right-click on your desktop and select “AMD Software: Adrenalin Edition”.
- Gaming Tab: Go to the “Gaming” tab, then select “Games”.
- Select Your Game: Choose the game you want to optimize or add it.
- AMD Anti-Lag: Toggle “Radeon Anti-Lag” to Enabled. This is your primary weapon against latency.
- Radeon Chill (Optional): Consider enabling “Radeon Chill” and setting a minimum/maximum FPS range. This can improve power efficiency and consistency without significant lag.
- Radeon Boost (Optional): For specific games, “Radeon Boost” dynamically lowers resolution during fast camera movements. This can further increase FPS and reduce lag, but may impact visual clarity.
- Apply Changes: Your settings are typically applied instantly.
Experiment with these settings. Every system and game can react differently. Find the sweet spot that gives you the best feel.
General Optimization Tips for Both Platforms
Beyond specific latency features, a few universal practices will further sharpen your setup.
- Monitor Refresh Rate: Ensure your monitor is set to its highest refresh rate in Windows display settings.
- In-Game Settings: Prioritize performance over graphics. Lowering settings like shadows, anti-aliasing, and post-processing can free up GPU resources.
- Disable V-Sync: Unless you experience severe screen tearing, keep V-Sync disabled. It often introduces input lag.
- Game Mode in Windows: Enable “Game Mode” in Windows settings. It helps prioritize game processes.
- Clean Background Processes: Close unnecessary applications running in the background. Every bit of CPU and RAM counts.
For more comprehensive system tuning, explore guides on reducing overall controller input lag and optimizing your PC.
The Impact of Low Latency Features
Curious about the actual difference these optimizations make? Data consistently shows significant reductions in system latency.
This translates to faster reaction times and a competitive edge.
A bar chart showing average system latency reduction in competitive games: NVIDIA Reflex (7ms) and AMD Anti-Lag (5ms), based on TechSpot data.
As seen, NVIDIA Reflex often provides a slightly greater reduction. However, both technologies are crucial for competitive play.
Test Your Latency Improvements on Joltfly
Theory is one thing, but real-world performance is what matters. After adjusting your settings, head over to Joltfly to measure your improvements.
Use our Mouse Polling Rate Test to ensure your mouse is reporting inputs consistently.
Then challenge your reaction speed with the Reaction Time Test. See how your optimized setup translates to faster responses.
Dominating your gaming circle starts with understanding your hardware. Fine-tune your settings, then prove your skills on Joltfly!
In Short
- Optimizing GPU driver settings with NVIDIA Reflex or AMD Anti-Lag is crucial for competitive gamers to reduce input latency and gain a decisive advantage.
- Both NVIDIA and AMD offer specific configurations within their control panels to enable features like “Low Latency Mode: Ultra” or “Radeon Anti-Lag” for individual games.
- General optimization tips for both platforms include updating drivers, ensuring high monitor refresh rates, prioritizing in-game performance, and disabling V-Sync.